Notice
Recent Posts
천천히 빛나는
삼성 SW 기출 문제 (2) 본문
본 포스팅에서는 [상어초등학교, 스타트택시, 마법사 상어와 파이어스톰, 마법사 상어와 비바라기]를 다룹니다.
21608. (상어 초등학교) 학생의 만족도의 총 합을 구해보자.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int N;
int classRoom[21][21];
int dx[] = { -1, 0, 0, 1 };
int dy[] = { 0, -1, 1, 0 };
struct Student
{
int s;
int sLike[4];
};
queue<Student>students;
Student resultRoom[21][21];
void assignSeat() {
int maxLike = -1;
int maxEmpty = -1;
pair<pair<int, int>, int > tempLike;
pair<int, int>tempEmpty;
Student now = students.front();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (classRoom[i][j] != 0)
continue;
int like = 0;
int empty = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
// 벗어남
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
// 비어있음
if (classRoom[nx][ny] == 0) {
empty++;
continue;
}
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++)
{
if (classRoom[nx][ny] == now.sLike[l]) {
like++;
break;
}
}
}
if (like > maxLike) {
maxLike = like;
tempLike.first.first = i;
tempLike.first.second = j;
tempLike.second = empty;
}
else if (like == maxLike) {
if (tempLike.second < empty) {
tempLike.first.first = i;
tempLike.first.second = j;
tempLike.second = empty;
}
}
if (maxEmpty < empty) {
maxEmpty = empty;
tempEmpty.first = i;
tempEmpty.second = j;
}
}
}
if (maxLike > 0) {
int x = tempLike.first.first;
int y = tempLike.first.second;
classRoom[x][y] = now.s;
resultRoom[x][y] = now;
}
else {
int x = tempEmpty.first;
int y = tempEmpty.second;
classRoom[x][y] = now.s;
resultRoom[x][y] = now;
}
students.pop();
}
void howMuch() {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
Student now = resultRoom[i][j];
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
// 벗어남
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++)
{
if (resultRoom[nx][ny].s == now.sLike[l]) {
cnt++;
break;
}
}
}
if (cnt != 0) {
result += int(pow(10, cnt - 1));
}
}
}
cout << result;
}
int main() {
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N*N; i++)
{
int s, s1, s2, s3, s4;
cin >> s >> s1 >> s2 >> s3 >> s4;
students.push({ s, {s1, s2, s3, s4} });
}
// 이자리는 항상 첫번째 학생 고정
classRoom[1][1] = students.front().s;
resultRoom[1][1] = students.front();
students.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < N * N - 1; i++)
{
assignSeat();
}
howMuch();
}classRoom은 그 칸에 누가 있는지 알려주는 배열이다. (0, 0)에 5가 저장되어 있으면 (0,0)에 5가 착석했다는 뜻이다.
queue strudents는 순서를 알려준다. front 순서대로 위치를 정하기 위해서 쓰는 자료구조이다.
resultRoom은 최종적으로 그 칸에 들어간 학생의 정보를 저장한다. 마지막에 만족도를 저장하기 위해서 만들었다.
21609. (상어 중학교) 오토 플레이가 모두 끝났을 때 획득한 점수의 합을 구해보자.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
int map[21][21];
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0 ,0, -1, 1 };
int result;
vector<pair<int, int>> vBlocks;
void gravity() {
for (int i = N-2; i >=0; i--)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N ; j++)
{
if (map[i][j] == -5 || map[i][j] == -1)
continue;
int x = i;
int y = j;
while (1) {
int nx = x + dx[1];
int ny = y + dy[1];
if (nx >= N)
break;
if (map[nx][ny] != -5)
break;
map[nx][ny] = map[x][y];
map[x][y] = -5;
x = nx;
y = ny;
}
}
}
}
void rotaion() {
int temp[20][20] = { 0, };
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
temp[i][j] = map[i][j];
}
}
// 90도 회전
for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
map[(N - 1) - j][i] = temp[i][j];
}
}
}
void remove() {
for (int i = 0; i < vBlocks.size(); i++)
{
int r = vBlocks[i].first;
int c = vBlocks[i].second;
map[r][c] = -5;
}
result += vBlocks.size() * vBlocks.size();
vBlocks.clear();
}
void findBlock() {
while (1) {
int cnt = 0;
int maxBlocks = -1;
int maxRanbows = -1;
int maxRows = -1;
int maxCols = -1;
bool visited_total[21][21] = { 0, };
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
{
// 이미 블럭에 포함되거나 벽임
if (visited_total[x][y] == 1 || map[x][y] <= 0)
continue;
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
vector<pair<int, int>> temp;
int color = map[x][y];
int blocks = 0;
int ranbows = 0;
bool visited[21][21] = { 0, };
q.push({ x, y });
temp.push_back({ x, y });
visited[x][y] = 1;
visited_total[x][y] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = r + dx[i];
int ny = c + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] == 0 && (map[nx][ny] == color || map[nx][ny] == 0)) {
q.push({ nx, ny });
blocks++;
temp.push_back({ nx, ny });
visited[nx][ny] = 1;
if (map[nx][ny] == 0)
ranbows++;
else
visited_total[nx][ny] = 1;
}
}
}
if (maxBlocks < blocks) {
maxBlocks = blocks;
maxRanbows = ranbows;
maxRows = x;
maxCols = y;
vBlocks = temp;
}
else if (maxBlocks == blocks) {
if (maxRanbows < ranbows) {
maxBlocks = blocks;
maxRanbows = ranbows;
maxRows = x;
maxCols = y;
vBlocks = temp;
}
else if (maxRanbows == ranbows) {
if (maxRows < x) {
maxBlocks = blocks;
maxRanbows = ranbows;
maxRows = x;
maxCols = y;
vBlocks = temp;
}
else if (maxRows == x) {
if (maxCols < y) {
maxBlocks = blocks;
maxRanbows = ranbows;
maxRows = x;
maxCols = y;
vBlocks = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (maxBlocks <= 0) // 블록이 없음
return;
remove();
gravity();
rotaion();
gravity();
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
findBlock();
cout << result;
}블럭이 하나도 남지 않았을 경우도 고려를 했어야 하는데 못해서 시간초과가 자꾸 났다. return이 되지 않아서 생기는 시간초과 오류였다.
19238. (스타트 택시) 모든 승객을 성공적으로 데려다줄 수 있는지 알아내고, 데려다줄 수 있을 경우 최종적으로 남는 연료의 양을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, M, G;
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int map[21][21];
int tX, tY;
struct TaxiInfo {
int sX;
int sY;
int dX;
int dY;
};
vector<TaxiInfo>taxi;
int Pickup() {
if (G <= 0)
return -1;
int visited[21][21] = { 0, };
queue <pair<int, int > > q;
q.push({ tX, tY });
visited[tX][tY] = 1;
int findIdx = 50000;
vector <pair<int, int > >nearTaxi;
while (!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (visited[r][c] > findIdx)
break;
if (map[r][c] >= 10) {
findIdx = visited[r][c];
nearTaxi.push_back({ r, c });
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = r + dx[i];
int ny = c + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] == 0 && map[nx][ny] != 1) {
q.push({ nx, ny });
visited[nx][ny] = visited[r][c] + 1;
}
}
}
if (nearTaxi.size() == 0)
return -1;
// 가까운 택시 찾음
sort(nearTaxi.begin(), nearTaxi.end());
int resultX = nearTaxi[0].first;
int resultY = nearTaxi[0].second;
int tInx = map[resultX][resultY];
map[resultX][resultY] = 0; // 픽업 완료
// 연료양이 충분함
if (G >= visited[resultX][resultY] - 1) {
// 충전
G -= (visited[resultX][resultY] - 1);
tX = resultX;
tY = resultY;
}
else {
G = 0;
return -1;
}
return tInx;
}
bool Arrival(int Ax, int Ay) {
if (G <= 0) {
return false;
}
int visited[21][21] = { 0, };
queue <pair<int, int > > q;
q.push({ tX, tY });
visited[tX][tY] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (r == Ax && c == Ay) {
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = r + dx[i];
int ny = c + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] == 0 && map[nx][ny] != 1 ) {
q.push({ nx, ny });
visited[nx][ny] = visited[r][c] + 1;
}
}
}
if (visited[Ax][Ay] == 0)
return false;
if (G >= visited[Ax][Ay] - 1) {
M--;
tX = Ax;
tY = Ay;
G += (visited[Ax][Ay] - 1);
return true;
}
else {
G = 0;
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> G;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
cin >> tX >> tY;
tX--;
tY--;
int sX, sY, dX, dY;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
cin >> sX >> sY >> dX >> dY;
taxi.push_back({ sX-1, sY-1, dX-1, dY-1 });
map[sX-1][sY-1] = i + 10;
}
while (M > 0) {
int pickUp = Pickup();
if (pickUp == -1) {
cout << -1;
return 0;
}
int Ax = taxi[pickUp - 10].dX;
int Ay = taxi[pickUp - 10].dY;
if (!Arrival(Ax, Ay)) {
cout << -1;
return 0;
}
}
cout << G;
return 0;
}자꾸 오타를 내서 틀린다. 벽이 -1이라고 자연스럽게 생각해서 -1로 Arrival 함수를 짰다가 오류가 났다. 문제를 읽고 제대로 정리해두는 습관을 만들어야겠다.
20058. (마법사 상어와 파이어스톰) 얼음이 있는 칸이 얼음이 있는 칸과 인접해 있으면, 두 칸을 연결되어 있다고 한다. 덩어리는 연결된 칸의 집합이다.
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int N, Q;
int L;
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
int A[65][65];
int total;
int part;
void findBiggest() {
bool visited[65][65] = { 0, };
unsigned int maxVal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
// 이미 한번 묶이거나 얼음이 녹아서 없음
if (visited[i][j] == 1 || A[i][j] <= 0)
continue;
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
vector<pair<int, int>>temp;
q.push({ i, j });
temp.push_back({ i, j });
visited[i][j] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().first;
int y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = x + dx[k];
int ny = y + dy[k];
// 범위 벗어남
if (nx < 0 || nx >= total || ny < 0 || ny >= total)
continue;
// 한번도 포함되지 않고, 얼음양이 0보다 큰 경우만
if (visited[nx][ny] == 0 && A[nx][ny] > 0) {
q.push({ nx,ny });
visited[nx][ny] = 1;
temp.push_back({ nx, ny });
}
}
}
if (maxVal < temp.size()) {
maxVal = temp.size();
}
}
}
cout << maxVal;
}
void iceMelting() {
int temp[65][65];
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
temp[i][j] = A[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
if (A[i][j] == 0)
continue;
int cnt = 0;
for (int k =0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= total || ny < 0 || ny >= total)
continue;
if (A[nx][ny] > 0)
cnt++;
}
if (cnt < 3) {
temp[i][j]--;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
A[i][j] = temp[i][j];
}
}
}
void rotation() {
int temp[65][65];
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
temp[i][j] = A[i][j];
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < total; k+=part)
{
for (int l = 0; l < total; l+= part)
{
int tempx = k;
int tempy = l;
for (int j = l; j < l+ part; j++)
{
for (int i = k + part - 1; i >= k; i--)
{
int sz = part - 1;
A[tempx][tempy] = temp[i][j];
tempy++;
}
tempy = l;
tempx++;
}
}
}
}
int restIce() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < total; j++)
{
sum += A[i][j];
}
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> Q;
total = int(pow(2, N));
for (int i = 0; i < pow(2,N); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <pow(2,N); j++)
{
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
vector<int>CMD;
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
CMD.push_back(x);
}
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++)
{
L = CMD[i];
part = int(pow(2, L));
rotation();
iceMelting();
}
cout << restIce() << '\n';
findBiggest();
}행렬 회전 이해가 부족해서 시간이 엄청 오래 걸렸다.
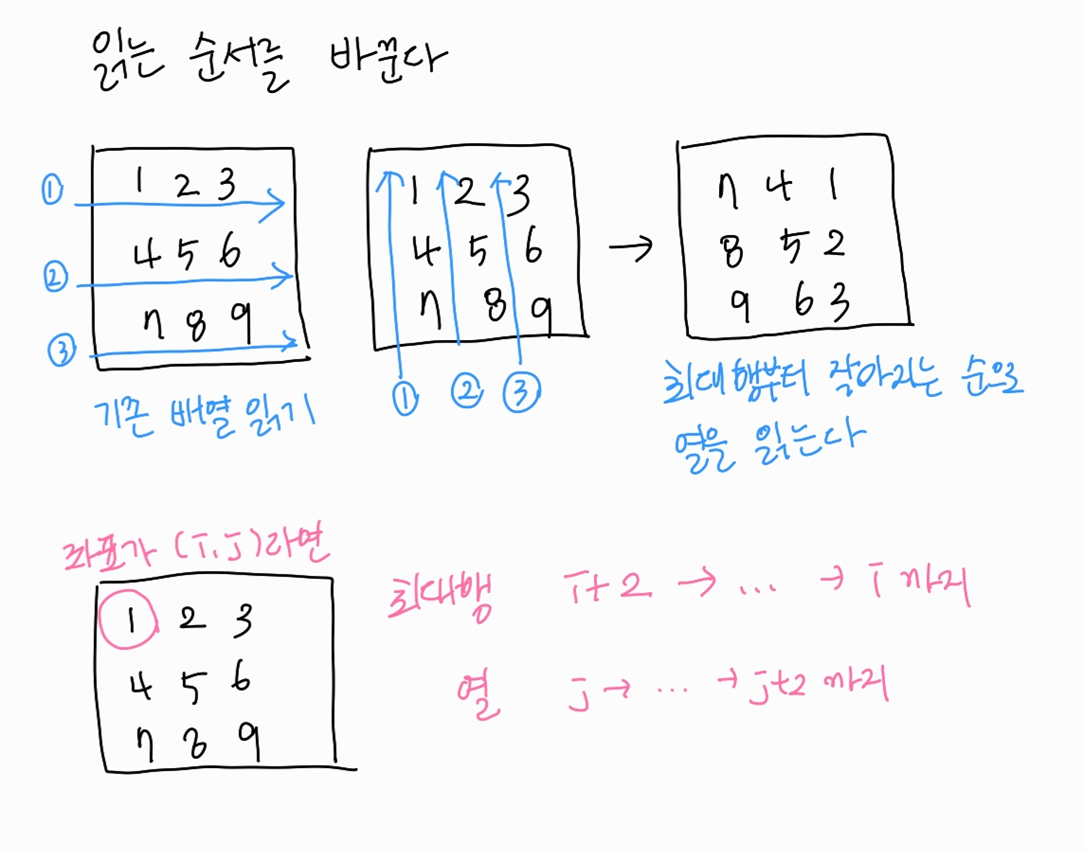
행렬 회전을 구현할 때 이와 같이 해야하는 것을 배웠다. 중요한 문제이다.
또 pow 함수가 생각보다 계산이 오래걸려서 따로 선언을 해주어야 시간초과가 나지 않는다. 앞으로 pow 함수를 자주 이용해야하는 상황에서는 따로 선언을 해주어야겠다.
21610. (마법사 상어와 비바라기) M번의 이동이 모두 끝난 후 바구니에 들어있는 물의 양의 합을 구해보자.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
int A[51][51];
int d, s;
bool Clouds[51][51];
// ←, ↖, ↑, ↗, →, ↘, ↓, ↙
int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int dy[] = { 0, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1 };
void Raining() {
vector<pair<int, int>> copyWater;
bool visited[51][51] = { 0, };
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
// 구름 없음
if (Clouds[i][j] == 0)
continue;
// 1. 모든 구름이 d 방향으로 s칸 이동한다
// N번 이동하면 위치 똑같음
int moving = s % N;
int nx = i + dx[d] * moving;
int ny = j + dy[d] * moving;
// 범위를 벗어나면 이어진 곳으로 이동
if (nx <= 0) {
nx += N;
}
else if (nx > N) {
nx -= N;
}
if (ny <= 0) {
ny += N;
}
else if (ny > N) {
ny -= N;
}
copyWater.push_back({ nx, ny }); // 물이 증가한 칸 저장
//구름이 있는 칸의 바구니에 저장된 물의 양이 1 증가함
A[nx][ny] += 1;
// 구름이 모두 사라짐
Clouds[i][j] = 0;
// 구름이 사라진 부분 표시
visited[nx][ny] = 1;
}
}
// 물복사버그 마법
for (int i = 0; i < copyWater.size(); i++)
{
int x = copyWater[i].first;
int y = copyWater[i].second;
// 대각선은 짝수에만 저장되어있음
for (int j = 2; j <= 8; j += 2)
{
int nx = x + dx[j];
int ny = y + dy[j];
// 범위를 벗어나는 칸 제외
if (nx <= 0 || nx > N || ny <= 0 || ny > N)
continue;
// 물이 있는 바구니 수만큼 증가
if (A[nx][ny] >= 1)
A[x][y]++;
}
}
// 바구니에 저장된 물이 2 이상인 칸에 구름이 생긴
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
// 구름이 생기는 칸은 구름이 사라진 칸이 되면 안된다
if (A[i][j] >= 2 && visited[i][j] == 0) {
Clouds[i][j] = 1; // 2 이상인 모든 칸에 구름이 생김
A[i][j] -= 2; // 물의 양이 2 줄어든다
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
// 비바라기 명령으로 비구름 생긴
Clouds[N][1] = 1;
Clouds[N][2] = 1;
Clouds[N - 1][1] = 1;
Clouds[N - 1][2] = 1;
// 각 양 입력받음
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
// 명령 시작
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
cin >> d >> s;
Raining();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
sum += A[i][j];
}
}
cout << sum;
}간단한 구현문제였다. 칸 수 이동문제가 나오면 %을 이용해서 구현하는 것이 좋다.

'C++ > SAMSUNG (C++)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 삼성 SW 기출 문제 (3) (0) | 2023.10.14 |
|---|---|
| 삼성 SW 기출 문제 (1) (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| 삼성 SW 기초 문제 (2) (4) | 2023.10.11 |
| 삼성 SW 기초 문제 (1) (1) | 2023.10.10 |





