천천히 빛나는
삼성 SW 기초 문제 (2) 본문
본 포스팅에서는 [주사위 굴리기, 아기상어, 나무 재테크, 2048, 낚시왕]을 다룹니다.
14499. (주사위 굴리기) 주사위는 지도의 바깥으로 이동시킬 수 없다. 만약 바깥으로 이동시키려고 하는 경우에는 해당 명령을 무시해야 하며, 출력도 하면 안 된다.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
int n, m, x, y, k;
int dx[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dice[7];
int map[20][20];
vector<int>cmd;
pair<int, int> now;
bool change(int d) {
int nx = now.first + dx[d - 1];
int ny = now.second + dy[d - 1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m)
return false;
if (d == 1) {
int temp = dice[3];
dice[3] = dice[1];
dice[1] = dice[4];
dice[4] = dice[6];
dice[6] = temp;
}
else if (d == 2) {
int temp = dice[4];
dice[4] = dice[1];
dice[1] = dice[3];
dice[3] = dice[6];
dice[6] = temp;
}
else if (d == 3) {
int temp = dice[2];
dice[2] = dice[1];
dice[1] = dice[5];
dice[5] = dice[6];
dice[6] = temp;
}
else {
int temp = dice[5];
dice[5] = dice[1];
dice[1] = dice[2];
dice[2] = dice[6];
dice[6] = temp;
}
now.first += dx[d - 1];
now.second += dy[d - 1];
cout << dice[1] << '\n';
return true;
}
void game() {
for (int i = 0; i < cmd.size(); i++)
{
if (change(cmd[i])) {
if (map[now.first][now.second] != 0) {
dice[6] = map[now.first][now.second];
map[now.first][now.second] = 0;
}
else {
map[now.first][now.second] = dice[6];
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> x >> y >> k;
now.first = x;
now.second = y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
while (k--) {
int s;
cin >> s;
cmd.push_back(s);
}
game();
}범위 밖을 벗어난 경우에도 복사를 하고 있지 않는지 살펴봐야하는 코드이다. void, return으로 처음에 구현했다가 틀렸길래 반례를 찾아보다 이런 오류를 발견하였다. 그래서 bool 타입으로 바꾸어주었다.
16236. (아기상어) 공간의 상태가 주어졌을 때, 아기 상어가 몇 초 동안 엄마 상어에게 도움을 요청하지 않고 물고기를 잡아먹을 수 있는지 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int n, x, y;
int map[20][20];
int sizeW = 2;
int cnt;
int tm;
int dx[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int dy[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
bool findFish() {
queue<pair<int,int>>q2;
q2.push({ x, y });
int visited[20][20] = {0, };
visited[x][y] = 1;
while (!q2.empty()) {
int oldr = q2.front().first;
int oldc = q2.front().second;
q2.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = oldr + dx[i];
int ny = oldc + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= n) {
continue;
}
if (visited[nx][ny]==0 && map[nx][ny] <= sizeW) {
q2.push({ nx, ny });
visited[nx][ny] = visited[oldr][oldc] + 1;
}
}
}
int minV = 1000;
int minx = 0;
int miny = 0;
int tempq = q.size();
int notgoing = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
if (visited[r][c] == 0) {
q.pop();
notgoing++;
continue;
}
if (minV > visited[r][c]) {
minV = visited[r][c];
minx = r;
miny = c;
}
else if (minV == visited[r][c]) {
if (r < minx) {
minV = visited[r][c];
minx = r;
miny = c;
}
else if (r == minx && c < miny) {
minV = visited[r][c];
minx = r;
miny = c;
}
}
q.pop();
}
if (notgoing == tempq) {
return false;
}
tm += (minV - 1);
map[minx][miny] = 0;
x = minx;
y = miny;
cnt++;
if (sizeW == cnt) {
sizeW++;
cnt = 0;
}
return true;
}
void findminLength() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (map[i][j] > 0 && map[i][j] != 9 && map[i][j] < sizeW) {
q.push({ i, j });
}
}
}
if (q.empty()) {
cout << tm;
return;
}
if (!findFish()) {
cout << tm;
return;
}
findminLength();
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 9) {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
map[x][y] = 0;
findminLength();
}현재 상어가 있는 곳에서 BFS -> 물고기 먹기 -> 먹을 수 있는 물고기가 없으면 프린트하고 종료
https://kau-algorithm.tistory.com/821
[백준/c++] 16236번 아기상어
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/16236 16236번: 아기 상어 N×N 크기의 공간에 물고기 M마리와 아기 상어 1마리가 있다. 공간은 1×1 크기의 정사각형 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 한 칸에는 물고기가 최대 1마리 존
kau-algorithm.tistory.com
위 티스토리에서 엄청 자세히 설명해두었으니 이해가 안된다면 위 티스토리를 읽으면서 구현해보는 것을 추천한다.
16235. (나무제테크) K년이 지난 후 상도의 땅에 살아있는 나무의 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m, k;
int x, y, z;
int map[11][11]; // 양분의 양
int A[11][11]; // 겨울에 추가할 양분의 양
deque<int>dq[11][11]; // 나이 저장
queue<int>die[11][11];
int dx[] = { -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 };
int dy[] = { -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1 };
void spring() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int tmp = dq[i][j].size();
for (int k = 0; k < tmp; k++)
{
if (map[i][j] >= dq[i][j].back()) {
map[i][j] -= dq[i][j].back();
dq[i][j].push_front(dq[i][j].back() + 1);
dq[i][j].pop_back();
}
else {
die[i][j].push(dq[i][j].back());
dq[i][j].pop_back();
}
}
}
}
}
void summer() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
while (!die[i][j].empty()) {
map[i][j] += (die[i][j].front() / 2);
die[i][j].pop();
}
}
}
}
void fall() {
queue<int>temp[11][11];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int tmp = dq[i][j].size();
for (int k = 0; k < tmp; k++)
{
if (dq[i][j].front() % 5 == 0) {
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++)
{
int nx = i + dx[l];
int ny = j + dy[l];
if (nx <= 0 || nx > n || ny <= 0 || ny > n) {
continue;
}
temp[nx][ny].push(1);
}
}
dq[i][j].push_back(dq[i][j].front());
dq[i][j].pop_front();
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
while (!temp[i][j].empty()) {
dq[i][j].push_back(1);
temp[i][j].pop();
}
}
}
}
void winter() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
map[i][j] += A[i][j];
}
}
}
void year() {
while (k--) {
spring();
summer();
fall();
winter();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
sum += dq[i][j].size();
}
}
cout << sum;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
map[i][j] = 5;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
cin >> A[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> x >> y >> z;
dq[x][y].push_back(z);
}
year();
}deque을 이용해서 구현했다.
12100. (2048-Easy) 이 문제에서 다루는 2048 게임은 보드의 크기가 N×N 이다. 보드의 크기와 보드판의 블록 상태가 주어졌을 때, 최대 5번 이동해서 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 블록의 값을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int map[21][21];
int n;
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
int maxV = 0;
bool moving(int x, int i, int j, int d, bool remain[][21]) {
int nx = i + dx[d];
int ny = j + dy[d];
// 끝까지 이동함
if (nx <= 0 || nx > n || ny <= 0 || ny > n) {
if (map[i][j] != 0)
return false;
map[i][j] = x;
return true;
}
// 블럭이 있으나 같지 않아서 이동을 못함
if (map[nx][ny] != 0 && map[nx][ny] != x) {
map[i][j] = x;
return false;
}
// 다음칸으로 이동할 수 있음
if (!remain[nx][ny]) {
// 다음칸에 블럭이 없음
if (map[nx][ny] == 0) {
moving(x, nx, ny, d, remain);
return true;
}
// 다음칸에 블럭이 있는데 합쳐질 수도 있음
else if (map[nx][ny] == x) {
map[nx][ny] += x;
remain[nx][ny] = 1;
return true;
}
}
// 다음칸에 이미 합쳐진 블럭이 있음
else {
map[i][j] = x;
return true;
}
return true;
}
void game(int direction, int cnt) {
if (cnt == 5) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
maxV = max(maxV, map[i][j]);
}
}
return;
}
bool visited[21][21] = { 0, };
if (direction == 2 || direction == 0) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
if (map[j][k] != 0) {
if (moving(map[j][k], j, k, direction, visited))
map[j][k] = 0;
}
}
}
}
else {
for (int j = n; j > 0; j--)
{
for (int k = n; k > 0; k--)
{
if (map[j][k] != 0) {
if (moving(map[j][k], j, k, direction, visited))
map[j][k] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int temp[21][21];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 1;j <= n; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <=n; k++)
{
temp[j][k] = map[j][k];
}
}
game(i, cnt + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
map[j][k] = temp[j][k];
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
int temp[21][21];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
temp[j][k] = map[j][k];
}
}
game(i, 0);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
map[j][k] = temp[j][k];
}
}
}
cout << maxV;
}이동방향을 잘 고려해야하는 문제였다.
17143. (낚시왕) 낚시왕이 상어 낚시를 하는 격자판의 상태가 주어졌을 때, 낚시왕이 잡은 상어 크기의 합을 구해보자.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int R, C, M; // m은 상어의 수
int r, c, s, d, z; // 위치, 속력, 이동 방향, 크기
// 1 상 2 하 3 우 4 좌
int kingY=1;
int catchsharksize = 0;
int map[101][101];
vector<int> shark[10001];
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int change_dir(int d) {
if (d == 1) return 2;
if (d == 2) return 1;
if (d == 3) return 4;
if (d == 4) return 3;
}
void catchShark() {
// cout << kingY << "초 입니다.\n";
// 상어 잡기
for (int i = 1; i <= R; i++)
{
if (map[i][kingY] != 0) {
// cout << catchsharksize << "획득\n";
catchsharksize += shark[map[i][kingY]][4];
shark[map[i][kingY]].clear();
map[i][kingY] = 0;
break;
}
}
vector<int> mvShark[101][101];
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++)
{
if (shark[i].size() > 0) {
int cnt = shark[i][2];
// 상어이동
map[shark[i][0]][shark[i][1]] = 0;
while (cnt--) {
int di = shark[i][3];
int nx = shark[i][0] + dx[di-1];
int ny = shark[i][1] + dy[di-1];
if (nx <= 0 || nx > R || ny <= 0 || ny > C) {
shark[i][3] = change_dir(di);
di = shark[i][3];
}
shark[i][0] += dx[di-1];
shark[i][1] += dy[di-1];
}
int mapx = shark[i][0];
int mapy = shark[i][1];
// 자리에 도착하려는 상어 저장
mvShark[mapx][mapy].push_back(i);
// cout << mapx << "," << mapy << "에 " << char('A' + i - 1) << " 가 들어가고 싶어함\n";
}
}
// 상어 충돌 시 계산
for (int i = 1; i <= R; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <=C; j++)
{
if (mvShark[i][j].size() > 0) {
//cout << i << "," << j << "에 들어오려는 상어가 있음\n";
int sharkNum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < mvShark[i][j].size(); k++)
{
int sharkTemp = mvShark[i][j][k]; // 상어번호
if (sharkNum == 0) {
sharkNum = sharkTemp;
}
else {
if (shark[sharkNum][4] < shark[sharkTemp][4]) {
//cout << "!!!!!여기!!!!!!!\n";
shark[sharkNum].clear();
sharkNum = sharkTemp;
}
else {
shark[sharkTemp].clear();
}
}
}
map[i][j] = sharkNum;
//cout << i << "," << j << "에 " << char('A'+sharkNum-1) << " 가 들어옴\n";
}
}
}
if (kingY == C)
return;
else {
kingY++;
catchShark();
}
}
int main() {
cin >> R >> C >> M;
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++)
{
cin >> r >> c >> s >> d >> z;
shark[i].push_back(r);
shark[i].push_back(c);
if (d == 1 || d == 2)
s %= ((R - 1) * 2);
if (d == 3 || d == 4)
s %= ((C - 1) * 2);
shark[i].push_back(s);
shark[i].push_back(d);
shark[i].push_back(z);
map[r][c] = i;
// cout << "상어 " << i << "가 들어감\n";
}
catchShark();
cout << catchsharksize;
}속도가 2R-2의 배수일 경우 원래 자리로 돌아오게 된다. (방향도 그래도)
그래서 2R-2로 나눠서 100 미만의 while문을 돌도록 했다. 상어가 10000마리인데 모두 1000번씩 이동하게 하면 10,000,000번 이동하게 되고 낚시왕이 100번 오른쪽으로 이동하면 1,000,000,000번으로 시간초과가 뜰 것이다.
이런 부분을 잘 이해하고 코드로 넣어야하지만 동작하는 코드이다.
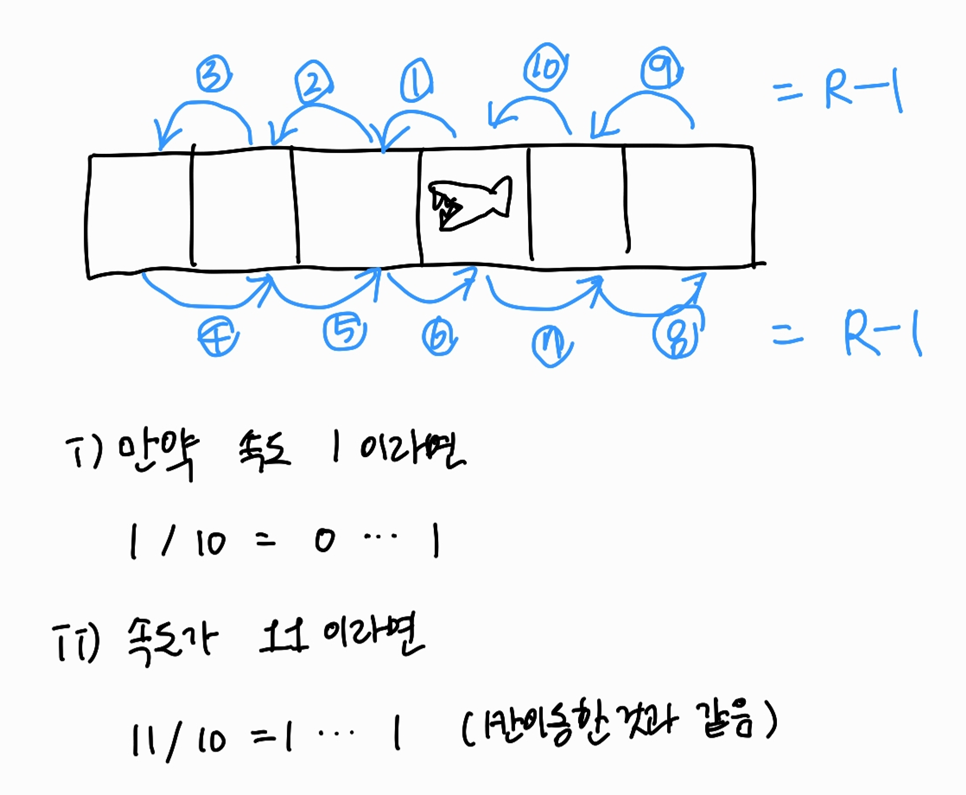
그림으로 나타내면 이와 같다.

https://www.acmicpc.net/workbook/view/7610
'C++ > SAMSUNG (C++)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 삼성 SW 기출 문제 (3) (0) | 2023.10.14 |
|---|---|
| 삼성 SW 기출 문제 (2) (1) | 2023.10.13 |
| 삼성 SW 기출 문제 (1) (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| 삼성 SW 기초 문제 (1) (1) | 2023.10.10 |





